In this tutorial, I will create a simple and practical example of how to provision EC2 instance with Github Actions and Terraform. I will use workflow_dispatch type of workflow which is triggered manually by the user, using Terraform Github action from HashiCorp.
Goal
Deploy EC2 instance of t2.micro size to your AWS account using Github Actions and Terraform.
I will use ‘workflow_dispatch’ event for this, which is manually triggered.
What is GitHub actions?
GitHub Actions is a continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) platform that allows you to automate your build, test, and deployment pipeline. You can create workflows that build and test every pull request to your repository, or deploy merged pull requests to production.
GitHub Actions goes beyond just DevOps and lets you run workflows when other events happen in your repository. For example, you can run a workflow to automatically add the appropriate labels whenever someone creates a new issue in your repository.
GitHub provides Linux, Windows, and macOS virtual machines to run your workflows, or you can host your own self-hosted runners in your own data center or cloud infrastructure.
workflow_dispatch
This event occurs when someone triggers a workflow run on GitHub or sends a
POSTrequest to the "Create a workflow dispatch event" endpoint. For more information, see "Events that trigger workflows."
Why use it?
GitHub Actions makes it easy to automate all your software workflows, now with world-class CI/CD. Build, test, and deploy your code right from GitHub. Make code reviews, branch management, and issue triaging work the way you want.
Let’s do it
we use the same credentials as the previous class
have the Access key id and Secret access key which will be added as secrets to Github repo.
The next step will be to add credentials to Github as secrets
Go to your Github repository -> settings -> secrets -> actions
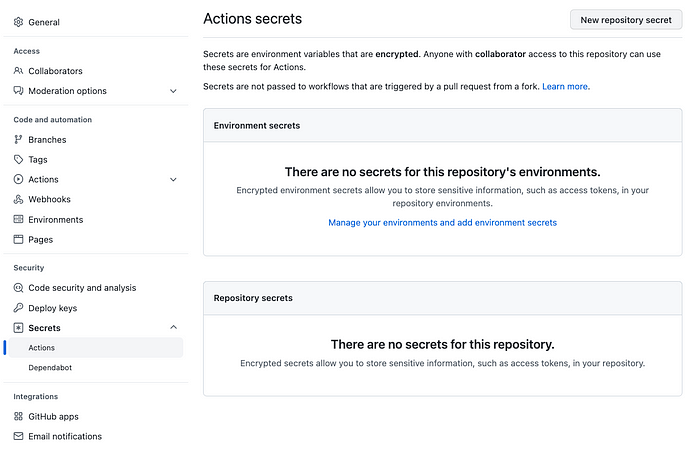
Add new repository secret
Need to add two secrets: AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY (Secret access key) which will be used later in the workflow
Add AWS_SECRET and also default region too in the same way.
Overview of the Terraform script to provision EC2 instance and install tomcat
- The provisioned instance is based on ubuntu
AMI. - The instance type is t2.micro.
- The instance will be provisioned to default VPC | subnet | security group.
- Need to use your previous key pair to connect with the provisioned instance.
- EC2 will be provisioned to ‘us-east-1’ region. (or Use your current region)
Generate SSH key pair to connect with EC2 instance
AWS console -> EC2 -> Key Pair -> Create Key Pair
To use this with github we need to create a S3 bucket so that we can use it to store our state file.
Terraform script to provision EC2 instance (put a name here)
# main.tf
# security.tf
Create a workflow with Github Actions to provision EC2 instance
- ‘configure-aws-credentials’ action used to set AWS credentials with docker container to be used by Terraform.
- You need to define name of EC2 instance using terraform variables: TF_VAR_ec2_name, before TF runs.
- Used setup-terraform action from HashiCorp.
- Used GitHub-hosted runner: ubuntu-latest.
To see your workflow in actions -> workflows, first need to create 2 files in ‘.github/workflows’ and add it to your repository.
# deploy.yml
#destroy.yml
I am using ‘workflow_dispatch’ type of workflow which is triggered manually.
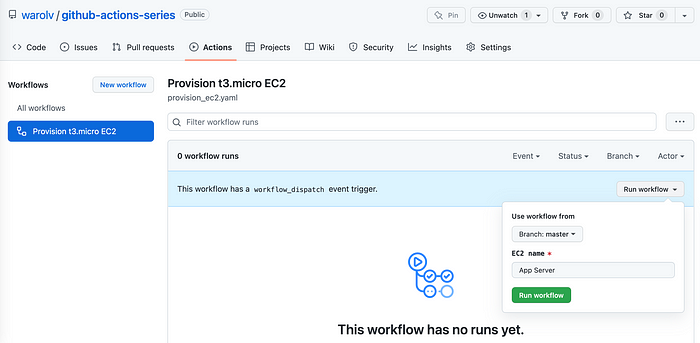
Click ‘Run workflow’
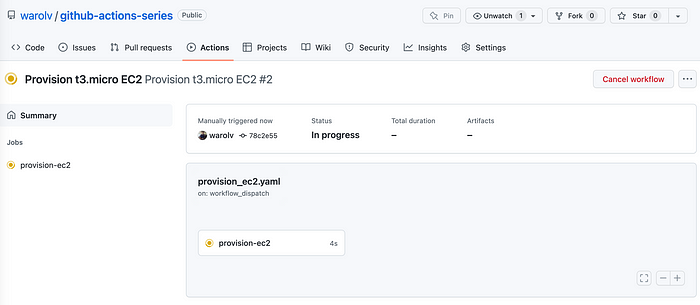
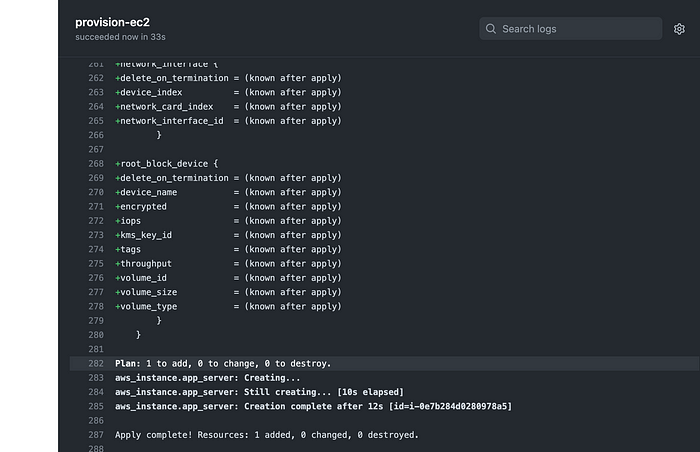
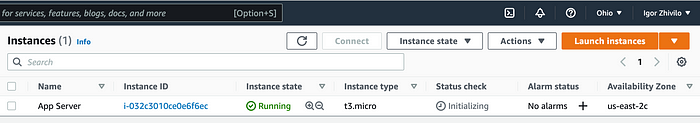
You can see using AWS console that EC2 instance created! and if you go to s3 bucket you created you will find the folder of the keyname you choose.
Now try to connect to this instance using ‘ur ssh key’
Success!
Conclusion
In this tutorial, I explained how to provision EC2 instances using Terraform and Github Actions workflow, I used GitHub-hosted runner and workflow_dispatch type of workflow which is triggered manually.



No comments:
Post a Comment